
What if you perform some erroneous keystrokes or mouse operations and the document ends up drastically modified in ways you didn’t intend?. To Paste, use Edit => Paste or Ctrl+V or click its button on the standard toolbar. Paste inserts the contents of the Clipboard into the document at the insertion point. To Copy, use Edit => or Ctrl+C or click its icon on the standard toolbar.Ĭut removes the selected portion from the document (but retains a copy of it in the Clipboard). To Cut, use Edit => Cut or Ctrl+X or click its icon on the standard toolbar. Each time you Cut or Copy a selected portion of the document, it is placed in the Clipboard (and replaces whatever was previously in the Clipboard). To understand these better, it is useful to know about the Clipboard. To duplicate a portion of the document, first use a Copy operation, then a Paste operation. To move a portion of the document from one location to another, you use a Cut operation followed by a Paste operation. 
Īnother way to select a whole document is to use the Edit => Select All command or type Ctrl+A. In Word, selected text is displayed on the screen as a reverse, which means, for example, that if it would ordinarily appear as black on white, it is instead displayed as white on black.
In this case, if no portion of the document is selected, the action is applied to the particular sub-unit where the insertion point happens to be. However, in Word, some actions only apply to a particular type of sub-unit of the document, like paragraphs, Specifying the object explicitly is called selection. #WHERE IS THE OUTLINE TEXT EFFECT IN WORD WINDOWS#
In Windows or any Windows application, you first specify what object you want to perform an action on, and then specify the action. You must also point the cursor to the desired location (once it’s visible) and click. Note that scrolling the Word window does not move the insertion point but only changes the part of the document that is displayed. Note: You can go to any of these and others. Edit => Go To… moves it to the beginning of the desired page, paragraph, section, etc. Ctrl+End: moves it to the end of the document. Ctrl+Home: moves it to the beginning of the document. Arrow keys: move it left, right, up, or down. Click: moves it to where the cursor is. In general, after typing some characters or performing a Paste or Insert operation, the insertion point is located just past the inserted text (or picture, e.g.). Note: It is not necessarily the same location as where the cursor is pointing, nor is it necessarily visible in the part of the document shown in the Word window. It is indicated by a blinking vertical bar. The insertion point is the location in the document where the next character typed will appear or the next Paste or Insert operation will deposit text or a picture, for example. To see or hide these or other toolbars, do View => Toolbars. Drawing toolbar: text box, arrow, etc. Formatting toolbar: bold, italic, underline, etc. Standard toolbar: new file, open file, save file, print, cut, copy, paste, etc. The most commonly used Word toolbars are:. Commonly used commands are collected into groups of buttons called toolbars. Lines, paragraphs, pages, and sections. The finished product is a professional-looking document with less effort. Other useful features: wizards and templates, automatic index and table of contents generation. 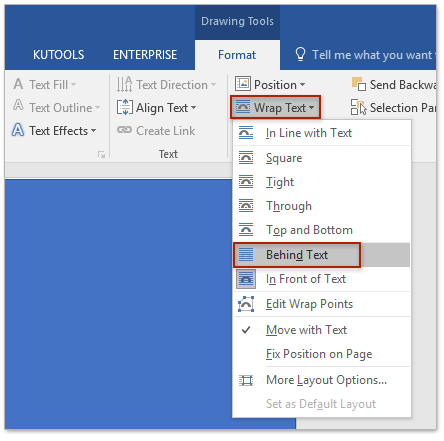 Modern word processors let you do any combination of these. Bottom up – throw ideas, sentences, phrases down, then build up from there.
Modern word processors let you do any combination of these. Bottom up – throw ideas, sentences, phrases down, then build up from there. 
Top down – create overall outline, then fill in the details. 






 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
